TECHNOLOGY
Exploring servidores de crack evolution docker : A Comprehensive Guide
In the fast-paced world of technology, staying ahead of trends and tools is crucial for anyone involved in server management and software development. A key player that has emerged over the years is Docker. This versatile tool has transformed how developers and IT professionals handle applications. If you’re part of the servidores de crack evolution docker community, understanding Docker’s role in server management is vital.
Understanding Servidores de crack evolution docker Rise
Docker’s emergence a few years ago marked a significant shift in software development. Before Docker, creating consistent environments across different stages of development was challenging. Docker changed the game by introducing containers, which encapsulate applications and their dependencies, ensuring they run uniformly regardless of where they’re deployed.
Docker’s appeal lies in its simplicity. It allows developers to package applications into containers, making it easier to manage and deploy across various platforms. This uniformity reduces the “it works on my machine” problem, streamlining processes and improving collaboration between development and operations teams.
Additionally, Docker’s ecosystem is continuously evolving, with new tools and integrations being introduced regularly. This adaptability means that Docker not only addresses current needs but is also poised to accommodate future technological shifts.
The Basics of Docker
For those new to Docker, it’s essential to grasp its foundational concepts. At its core, Docker uses containerization, a lightweight form of virtualization that allows multiple containers to run on a single host machine. Each container is isolated but can share the host’s OS kernel, leading to efficient resource utilization.
Containers are created from Docker images. These images are lightweight, standalone, and executable packages that include everything needed to run a piece of software, including code, runtime, system tools, and libraries. The beauty of Docker images is their portability—once an image is created, it can be run on any machine that supports Docker.
Docker Hub, the official repository for Docker images, is another critical component. It hosts a vast array of images, from official repositories curated by Docker to community-contributed images. Users can pull these images to create containers or push their images to share with the community.
Why Docker Matters in Server Management
Server management is a complex task, often involving multiple applications, each with its unique dependencies. Docker simplifies this by allowing each application to run in its container, isolated from others. This isolation prevents conflicts and makes it easier to manage resources.
Furthermore, Docker’s consistency means that once an application runs smoothly in a container, it will work across all environments—development, testing, and production. This consistency reduces the chances of unexpected issues arising when moving applications to different servers.
Docker also enhances scalability. Containers can be easily scaled up or down based on demand. This flexibility is crucial in today’s dynamic business environments, where the ability to respond quickly to changes can be a significant competitive advantage.
Exploring Docker’s Impact on Application Development
Docker has revolutionized application development by enabling DevOps practices. With Docker, developers can test their applications in environments identical to production settings, reducing the chances of encountering environment-specific bugs.
Continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines significantly benefit from Docker. By integrating Docker into these pipelines, developers can automate the building, testing, and deployment of applications, ensuring faster and more reliable releases.
Furthermore, Docker’s lightweight nature means that developers can run multiple containers on a single machine, making it easier to test various versions of an application or run microservices architectures. This architecture allows for modular applications, where each service can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
Best Practices for Docker Implementation
Implementing Docker successfully requires following best practices to maximize its benefits. First, it’s crucial to keep Docker images lean. Avoid unnecessary software and libraries in your images to reduce size and improve performance.
Version control is another essential practice. Tag your Docker images with meaningful version numbers to ensure consistency and traceability, especially in environments with rapid development cycles.
Security is always a concern in server management. Regularly update your Docker images to incorporate the latest security patches. Additionally, scan images for vulnerabilities using tools like Clair or Trivy to maintain a robust security posture.
Docker’s Role in Continuous Deployment
In continuous deployment, Docker plays an integral role by providing a consistent environment from development to production. This consistency ensures that applications tested in a staging environment behave identically when deployed live.
Deployments become predictable, and rollback processes are simplified. If an issue arises, reverting to a previous Docker image is straightforward, minimizing downtime and disruption.
Docker’s compatibility with orchestration tools like Kubernetes further enhances its role in deployment. These tools automate deploying, scaling, and managing containerized applications, allowing teams to focus on building features rather than managing infrastructure.
The Community Behind Docker
Docker’s success is partly due to its vibrant community. This community contributes to a rich repository of Docker images, plugins, and integrations that extend Docker’s functionality.
Forums, meetups, and conferences provide avenues for knowledge sharing and collaboration. Engaging with this community can offer valuable insights and solutions to common challenges faced when working with Docker.
Open-source contributions also play a significant role. Developers can contribute code, report issues, or enhance documentation, ensuring Docker continues to evolve to meet the community’s needs.
Future Trends in Docker and Server Management
The future of Docker looks promising, with several trends emerging. One trend is the increased use of multi-cloud environments. Docker’s portability makes it ideal for deploying applications across different cloud providers, maximizing flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Another trend is serverless computing, where developers focus on writing code without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. Docker’s ability to containerize applications aligns well with serverless architectures, offering a bridge between traditional servers and serverless deployments.
Finally, as AI and machine learning continue to grow, Docker will play a role in managing the environments needed for these applications, ensuring they have the necessary resources and dependencies to function optimally.
Challenges and Solutions with Docker
Like any technology, Docker poses challenges that users must address. Managing persistent data in containers can be tricky since containers are stateless by nature. Solutions include using Docker volumes or integrating with external storage solutions to maintain data integrity.
Networking is another potential challenge. Configuring communication between containers, especially in complex architectures, requires careful planning. Docker provides networking tools to facilitate this, but understanding these tools is crucial for effective implementation.
Resource management is essential in environments with numerous containers. Tools like cgroups and Docker’s resource constraints allow administrators to allocate CPU and memory resources efficiently, preventing overconsumption.
Maximizing Docker’s Potential
To truly harness Docker’s capabilities, organizations must integrate it with complementary tools and workflows. Monitoring solutions like Prometheus or Grafana can provide insights into container performance, helping identify bottlenecks and optimize resource utilization.
Log aggregation tools like ELK Stack or Graylog can centralize logs from multiple containers, simplifying troubleshooting and analysis. These tools fit seamlessly with Docker’s architecture, ensuring a cohesive operational environment.
Training and upskilling are also vital. Providing team members with the necessary knowledge and skills ensures they can leverage Docker effectively, maximizing its impact on the organization’s operations.
Docker vs. Traditional Virtualization
Docker and traditional virtualization both serve to isolate applications, but they do so differently. Virtual machines (VMs) provide complete OS-level isolation, while Docker containers share the host OS.
This difference results in Docker being more lightweight and efficient, as containers require fewer resources than VMs. However, VMs offer greater isolation, which can be beneficial in specific scenarios where security is paramount.
Choosing between Docker and traditional virtualization depends on the specific needs and constraints of the organization. In many cases, a combination of both technologies can provide a balanced solution.
Conclusion
Servidores de crack evolution docker has become an indispensable tool in the world of server management and application development. Its ability to simplify processes, enhance collaboration, and improve deployment consistency makes it a valuable asset for any organization.
By understanding Docker’s capabilities and integrating it into your workflows, you can unlock new levels of efficiency and innovation. Engage with the Docker community, explore emerging trends, and continue to refine your Docker skills to stay ahead in the fast-evolving landscape of technology.
If you’re ready to take the next step, explore Docker further and see how it can transform your operations. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your Docker journey, there’s always more to learn and discover.
TECHNOLOGY
Key Features of HONOR Magic 7 Pro Camera
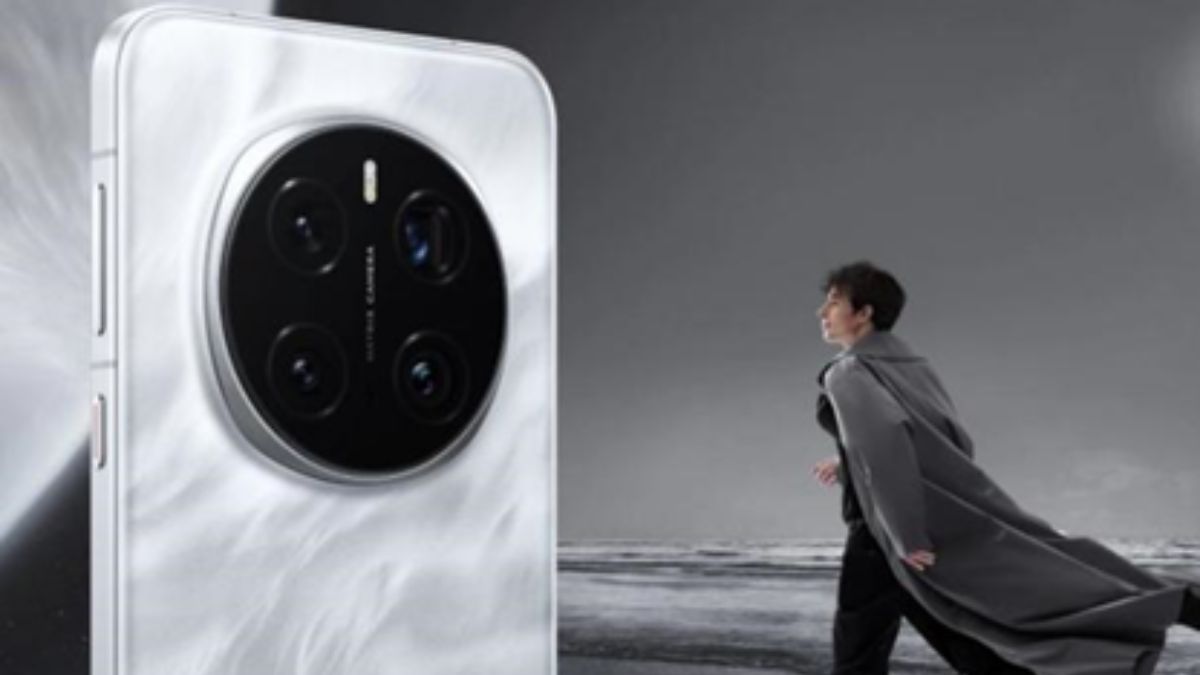

Dive into the world of mobile photography with the HONOR Magic 7 Pro, designed to transform your everyday photos into professional-quality images. Equipped with cutting-edge technology, the Magic 7 Pro camera system promises to capture stunning details and vibrant colors in every shot. Whether you are an amateur photographer or a seasoned professional, this ultimate guide will explore the key features of the HONOR Magic 7 Pro camera to help you make the most out of your photography experience.

What Are the Key Camera Specs of HONOR Magic 7 Pro?
Rear Camera Configuration
At the heart of the HONOR Magic 7 Pro is a sophisticated rear camera setup that includes a powerful 50MP Super Dynamic HONOR Falcon Camera with an aperture of f/1.4 and f/2.0, equipped with Optical Image Stabilization (OIS). This is complemented by a 50MP Ultra Wide Camera with an aperture of f/2.0, ideal for capturing expansive landscapes and group photos. The highlight is the 200MP Telephoto Camera featuring an aperture of f/2.6, 3x Optical Zoom, and 100x Digital Zoom capabilities, allowing you to capture incredible details even from a distance. This combination ensures versatility and superior image quality in various shooting scenarios.
Front Camera Features
The front camera setup on the HONOR Magic 7 Pro is just as impressive with a 50MP camera featuring an f/2.0 aperture, joined by a 3D Depth Camera that enhances portrait shots with realistic bokeh effects. This setup supports advanced features like 3D face unlock for added security and ease of use. With an image resolution of 8192 x 6144 pixels, the front camera guarantees crisp and vibrant selfies, making it perfect for social media enthusiasts and vloggers alike.
Camera Modes and Features
The HONOR Magic 7 Pro comes packed with an array of camera modes and features to suit every photography need. These include HD Super Burst, AI Enhanced Portrait, AI Super Zoom, Stage Mode, Motion Sensing Capture, and Smart Focus. Other notable features include Night Mode, Super Macro, Pro Mode, Panorama, Filter, Watermark, and Story Mode for crafting creative photos and videos. With both EIS and OIS stabilization modes, your videos and images remain blur-free and sharp, no matter the conditions.

How Does the HONOR Magic 7 Pro Perform in Low Light Conditions?
Night Photography Capabilities
When it comes to low light performance, the HONOR Magic 7 Pro excels with its Night Mode, which significantly enhances image clarity and detail even in poorly lit environments. The large aperture of the 50MP rear camera ensures ample light intake, reducing noise and producing bright, vivid photos. The 200MP Telephoto Camera, with its high resolution and powerful zoom, captures distant subjects clearly even in low light, making it an excellent choice for night photography.
AI-enhanced Features for Low Light
The camera’s AI-enhanced features automatically adjust settings based on the surrounding light conditions. This includes the AI Super Wide Angle, which maximizes the field of view while maintaining brightness and detail in low-light settings. These intelligent adjustments help reduce noise and enhance color accuracy, ensuring your night-time photos are as breathtaking as those taken during the day. The HONOR Magic 7 Pro’s AI capabilities make low-light photography effortless, allowing you to focus on framing the perfect shot.
What Makes HONOR Magic 7 Pro’s Video Recording Stand Out?
4K Video Recording Capabilities
The HONOR Magic 7 Pro stands out with its ability to record videos in stunning 4K resolution at 60fps, providing rich detail and smooth motion. This high frame rate is perfect for capturing fast-moving subjects without losing clarity. Whether you are documenting a sports event or creating a cinematic vlog, the 4K video recording capability ensures your videos look professional and immersive.
Video Modes and Features
The device offers a variety of video modes to enhance your recording experience. These include Slow-Mo, which captures high-speed action in slow motion, Time-lapse for compressing extended events into short clips, and Movie Mode for applying cinematic effects. The Multi-video mode allows you to simultaneously capture footage from the front and rear cameras, offering dynamic perspectives in your videos. With these features, the HONOR Magic 7 Pro is an ideal tool for budding videographers and content creators.
Front Camera Video Quality
The front camera is equally capable of capturing high-quality videos, supporting 4K video recording. This feature is particularly beneficial for vloggers and content creators who rely on front-facing videos. The added 3D Depth Camera ensures that portrait videos are enhanced with smooth background blur, making the subject stand out with a professional touch. Whether you are recording tutorials, live streaming, or simply capturing moments, the front camera of the HONOR Magic 7 Pro delivers excellent video quality.
How Do the AI Features Enhance the HONOR Magic 7 Pro Camera Experience?
AI for Portraits and Selfies
AI technology in the HONOR Magic 7 Pro plays a significant role in taking your portraits and selfies to the next level. The AI Enhanced Portrait mode intelligently analyses facial features and lighting conditions to produce natural-looking skin tones and enhanced details. The AI also assists in creating stunning bokeh effects, where the background is beautifully blurred while the subject remains in sharp focus. This ensures every selfie and portrait looks professionally shot.
AI for Smart Focus and Scene Recognition
The AI Smart Focus feature automatically tracks and focuses on moving subjects, ensuring they remain in sharp focus throughout. This is particularly useful for capturing action shots and dynamic scenes. Scene Recognition, another powerful AI feature, adjusts the camera settings in real-time based on the detected scene—whether it’s a sunset, a snowy landscape, or a bustling city street. This results in images that are perfectly exposed and color-balanced, regardless of the shooting environment.
AI Super Zoom and Motion Sensing
AI Super Zoom enhances the camera’s zoom capabilities, providing clear and detailed images even at high magnification levels. The Motion Sensing feature detects motion in the frame and adjusts the shutter speed and ISO settings to prevent blur, ensuring fast-moving subjects are captured with precision. These AI-driven enhancements make the HONOR Magic 7 Pro an incredibly versatile camera phone, capable of tackling a wide range of photographic challenges.
Conclusion
The HONOR Magic 7 Pro is a remarkable camera phone packed with advanced features that cater to both photography enthusiasts and professionals. From its powerful rear and front camera configurations to its impressive low-light performance and 4K video recording capabilities, the Magic 7 Pro sets a new standard in mobile photography. With the aid of AI-enhanced features, capturing stunning photos and videos has never been easier. If you are looking for a smartphone that delivers exceptional camera performance, the HONOR Magic 7 Pro buy online option should undoubtedly be at the top of your list.
TECHNOLOGY
Nidwaldner Gemeinden Software Wasserversorgung

When it comes to efficient water management for municipalities, tailored software solutions play a critical role. One such solution, Nidwaldner Gemeinden Software Wasserversorgung, is transforming the way local governments manage water supply systems. This innovative software combines advanced technology with user-friendly interfaces to help municipalities ensure optimal water usage, improve resource management, and maintain regulatory compliance.
Whether you’re a policymaker, city manager, or IT professional charged with public infrastructure, understanding this software and its capabilities can help you make informed decisions. This detailed blog will provide a clear overview of the Nidwaldner Gemeinden Software Wasserversorgung, its key features, and the immense benefits it offers.
What is Nidwaldner Gemeinden Software Wasserversorgung?
Nidwaldner Gemeinden Software Wasserversorgung, designed specifically for municipalities in the Canton of Nidwalden, Switzerland, is a comprehensive software solution aimed at streamlining water management systems. It enables municipalities to manage water supply networks, monitor consumption, and ensure sustainable usage through advanced data and system integrations. Its focus on usability and compliance makes it an indispensable tool for modern water system management.
Why Effective Water Management Software Matters
Water is one of the most essential resources for human life and local development. However, as climate change, urban growth, and aging infrastructure create challenges, having an efficient and dynamic water management system becomes mandatory. Software like Nidwaldner Gemeinden Software Wasserversorgung helps municipalities solve complex water supply issues by:
- Ensuring water quality through proper monitoring.
- Preventing wastage by delivering granular data for leaks and overflows.
- Streamlining resource planning with insights from real-time data.
- Remaining compliant with local and national water-use regulations.
Key Features of Nidwaldner Gemeinden Software Wasserversorgung
To better understand the power of this software, here’s a breakdown of its standout features:
1. Real-Time Data Monitoring
- Get live updates on water usage, demand fluctuations, and supply metrics.
- Centralized dashboards provide an easy overview of all crucial metrics.
- Automated alerts inform users of irregularities in water systems, empowering faster responses.
2. Leak Detection and Maintenance Planning
- Uses predictive algorithms to identify areas at risk of leaks or bursts.
- Reduces response time, minimizing water loss and infrastructure damage.
- Generates maintenance schedules for pumps, pipes, and key water system assets.
3. Comprehensive Reporting
- Create accurate, regulatory-compliant water reports for government bodies.
- Access historical water usage data to help plan long-term strategies.
- Generate customizable reports for diverse stakeholders, ensuring complete transparency.
4. User-Friendly Interfaces
- Designed specifically for municipal users with varying technical expertise.
- Features intuitive navigation, ensuring minimal training needs.
- Multi-language support accommodates diverse municipal teams.
5. Data Integration Capabilities
- Integrates seamlessly with GIS mapping tools for infrastructure visualization.
- Merges with other municipal management tools like finance and energy management systems.
- Scales flexibly with increasing data demands and municipal expansion.
6. Sustainability Features
- Tracks ecological indicators to promote environmentally friendly water usage.
- Supports decision-making for conservation through predictive modeling.
- Encourages compliance with international sustainable development standards.
How Nidwaldner Gemeinden Software Wasserversorgung Benefits Municipalities
This software can be a game changer for municipalities in Nidwalden and beyond. From small villages to larger urban centers, its benefits cater to the diverse needs of water management operations:
1. Improved Efficiency
By automating routine tasks like system monitoring and report generation, municipalities save valuable time and resources. This allows staff to focus on more strategic activities, such as planning for future water needs.
2. Cost Savings
Leak detection and predictive maintenance mean fewer costly emergencies. Meanwhile, actionable insights into consumption patterns help municipalities plan investments wisely.
3. Stronger Compliance
With detailed and tailored reports at your fingertips, staying compliant with complex Swiss water regulations becomes easier than ever.
4. Citizen Satisfaction
Reliable water supply systems, combined with improved service response times, lead to happier residents and businesses.
5. Environmental Benefits
Proactive water conservation measures contribute to sustainability goals, ensuring water resources are preserved for future generations.
Examples of Applied Success
Municipalities already using Nidwaldner Gemeinden Software Wasserversorgung have reported impressive results. For example:
- Municipality A reduced water loss by 15% within six months of adopting the software by identifying and repairing underground leaks faster.
- Municipality B streamlined its report compilation process by 50%, freeing up resources to focus on community engagement.
- Municipality C achieved compliance with new local water regulations in record time, avoiding penalties.
Steps to Implement Nidwaldner Gemeinden Software Wasserversorgung
Implementing this software may seem complex, but following a structured process ensures smooth adoption:
Step 1. Assess Your Needs:
Understand your municipality’s unique water management challenges and specific technical requirements.
Step 2. Engage Key Stakeholders:
Get input from water system operators, financial officers, and IT teams.
Step 3. Run a Trial:
Request a demonstration or trial period to see how it integrates within your existing operations.
Step 4. Train Your Team:
Provide comprehensive training to ensure your municipal team can use the software efficiently.
Step 5. Monitor and Optimize:
After implementation, consistently monitor performance to make sure you’re maximizing its capabilities.
The Future of Water Systems with Nidwaldner Gemeinden Software
Water management is increasingly reliant on data-driven solutions, and software like Nidwaldner Gemeinden Software Wasserversorgung is setting the bar high. With its dynamic features, sustainable approach, and user-friendly design, this software promises to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and transform how municipalities manage water systems.
Adopting such technology today is not only a strategic move but also a forward-thinking investment in the future of municipal infrastructure—and the communities they serve.
TECHNOLOGY
MSB247: Your All-in-One Solution

Managing a business involves countless moving parts—team coordination, workflow oversight, financial handling, and more. What if we told you there’s a tool that takes the chaos out of business management? Enter MSB247, your comprehensive all-in-one software solution.
Whether you’re a small startup or a growing enterprise, MSB247 streamlines operations, helps teams collaborate more effectively, and enhances overall productivity—all from a single platform.
Curious about why MSB247 is garnering attention among businesses worldwide? Keep reading to discover how it can revolutionize your workflow.
What is MSB247?
MSB247 is a robust, all-in-one management software tailored to help organizations oversee and optimize daily operations, project workflows, finance, and employee management under one platform.
No more juggling multiple tools for various tasks—MSB247 consolidates everything you need in one place to create a seamless experience for you and your team.
Why Is an All-in-One Solution Important?
Using disparate tools to manage your business often leads to inefficiency. Systems don’t integrate smoothly, key data may get lost between platforms, and employees spend too much time navigating multiple apps rather than focusing on the tasks at hand.
MSB247 solves this problem. It offers everything you need in one interface, centralizing your operations so you can concentrate on scaling up rather than sorting files.
Key Features of MSB247
MSB247 offers a wide array of features designed to fit seamlessly into your business operations. Here’s everything you need to know about the core features powering this platform.
1. Comprehensive Task Management
Organizing workflows no longer needs to be a headache. MSB247 allows you to assign and prioritize tasks while offering project tracking tools to keep everyone aligned.
- Create, assign, and track tasks in real time.
- Set deadlines and monitor progress through an intuitive dashboard.
- Color-coded labels and filters for better organization.
With task clarity and accountability, your team can stay focused on completing projects efficiently.
2. Financial Oversight Made Simple
Tired of messy accounting spreadsheets? MSB247 simplifies the financial side of your business with effective tools for managing income, expenses, and budgets.
- Generate professional invoices in just a few clicks.
- Track revenue streams and examine detailed financial reports.
- Automate recurring payments and monitor expenditure effortlessly.
This tool provides the transparency you need to make informed financial decisions.
3. Streamlined Communication Tools
Communication breakdown is a common problem for teams working in different locations. MSB247 bridges the gap with streamlined features designed for effective collaboration.
- Built-in conversations to eliminate the need for external email chains.
- Instant messaging for quick updates.
- Secure file sharing for documents, spreadsheets, and more.
Clear communication is the key to team success, and MSB247 ensures everyone is on the same page.
4. Employee Management Features
Managing a team takes effort, but MSB247 makes it easier by providing tools to oversee employee performance and manage schedules.
- Track attendance, leave, and hours worked effectively.
- Streamline the onboarding process for new hires.
- Monitor team workflows and adjust resources as needed.
MSB247 empowers you to become a better leader by providing insights into your team’s productivity and engagement.
5. Data Security at Its Core
Data security is a priority for any organization—and MSB247 takes it seriously. Its security protocols ensure that sensitive information stays protected.
- Secure cloud storage for all your data.
- Encryption features to maintain confidentiality.
- Regular updates to meet the latest security standards.
With MSB247, you can trust that your business information is only accessible to those who need it.
6. Customizable for Your Business Needs
Every business is unique, and MSB247 understands this. The platform offers customizable dashboards and features to suit your specific operational style.
- Choose the modules you need and hide what you don’t.
- Adapt workflows to reflect organizational changes.
- Personalize reports to highlight the most crucial data points.
From startups to large organizations, MSB247 grows with your business and adapts to its evolving requirements.
How MSB247 Benefits Businesses
Why are so many businesses turning to MSB247? The platform delivers tangible benefits that translate into saved time, decreased costs, and improved efficiency.
Save Time and Eliminate Redundancy
By consolidating all operations under one platform, MSB247 reduces the time employees waste switching between tools and platforms.
Boost Team Productivity
The seamless communication and task automation features create a unified workflow that keeps everyone focused and motivated.
Improve Decision-Making Through Insights
Access to detailed data and analytics enables leadership teams to make smarter, well-informed decisions.
Cost-Efficient Option
Investing in MSB247 means eliminating the need for multiple software subscriptions, which cuts operating costs significantly.
Testimonials from Satisfied Customers
Here’s what businesses are saying about MSB247’s impact on their operations.
“Switching to MSB247 has made all the difference for our team. Managing projects and tracking finances under one system keeps us organized and on track.”
— Lisa M., Operations Manager
“MSB247 transformed the way we work! The communication tools and task tracker saved us hours every week. Highly recommend it to any business owner.”
— James T., CEO
“We’ve seen a 35% productivity increase since adopting MSB247. It’s an all-in-one solution that delivers on its promises.”
— Priya R., HR Lead
Getting Started with MSB247
Transitioning to MSB247 is quick and easy. Here’s how you can get started today.
- Sign Up Free: Create an account and explore the tools with a free trial.
- Set Up Your Dashboard: Tailor it to match your workflows and priorities.
- Onboard Your Team: Add users and share a quick guide on leveraging MSB247’s features.
- Dive Into Efficiency: Start reaping the benefits of having all your operations in one place.
[Sign Up for Free](#) today and experience the all-in-one solution designed to propel your business forward.
Why MSB247 Is an Investment in Success
Running a business is challenging, but MSB247 eases the burden by taking care of the operational complexities. Whether you’re mapping out next quarter’s projects, managing payroll, or strategizing for growth, MSB247 equips you with the tools to succeed.
The bottom line? MSB247 isn’t just a tool—it’s a partner in your business’s success.
-

 BLOG11 months ago
BLOG11 months agoTribute Printed Pics: Top 10 Ways to Honor Loved Ones
-

 NEWS11 months ago
NEWS11 months agoNEWS JoTechGeeks: How to Stay Updated with the Latest News
-

 BLOG9 months ago
BLOG9 months agoThe //Vital-Mag.net Blog: Your Daily Dose of Inspiration
-

 HEALTH11 months ago
HEALTH11 months ago2023-1954: Enhancing Health and Vitality
-

 ENTERTAINMENT11 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT11 months agoFreemoviesfull.cc: Ultimate Guide
-

 TECH11 months ago
TECH11 months agoWww abithelp .com: Your Ultimate Online Assistance Platform
-

 HEALTH11 months ago
HEALTH11 months agowww healthsciencesforumcom: A Trusted Health Sciences Platform
-

 TECH10 months ago
TECH10 months agoCar Review Miracoup: Unveiling the Latest Features and Performance
